 We’ve
locked a lot of people up since 1980,
making
the U.S. the world leader in prison population (both total and per capita),
and the south the leader of the U.S.
Locking up a lot of non-violent offenders, especially drug offenders,
hasn’t bought us much safety and has caused a lot of problems.
We’ve
locked a lot of people up since 1980,
making
the U.S. the world leader in prison population (both total and per capita),
and the south the leader of the U.S.
Locking up a lot of non-violent offenders, especially drug offenders,
hasn’t bought us much safety and has caused a lot of problems.
Fortunately, somebody is trying to do something about it:
Washington, DC–Senator Jim Webb (D-VA) today introduced bipartisan legislation to create a blue-ribbon commission charged with conducting an 18-month, top-to-bottom review of the nation’s entire criminal justice system and offering concrete recommendations for reform. Senator Arlen Specter (R-PA), Ranking Member on the Judiciary Committee, is the principal Republican cosponsor.You can follow the progress of S.714 online; it’s currently before the Senate Judiciary Committee.
Meanwhile, Jim Webb explains the problem in Parade:
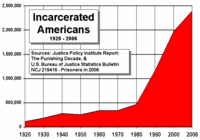
America’s criminal justice system has deteriorated to the point that it is a national disgrace. Its irregularities and inequities cut against the notion that we are a society founded on fundamental fairness. Our failure to address this problem has caused the nation’s prisons to burst their seams with massive overcrowding, even as our neighborhoods have become more dangerous. We are wasting billions of dollars and diminishing millions of lives.We need to fix the system. Doing so will require a major nationwide recalculation of who goes to prison and for how long and of how we address the long-term consequences of incarceration. Twenty-five years ago, I went to Japan on assignment for PARADE to write a story on that country’s prison system. In 1984, Japan had a population half the size of ours and was incarcerating 40,000 sentenced offenders, compared with 580,000 in the United States. As shocking as that disparity was, the difference between the countries now is even more astounding–and profoundly disturbing. Since then, Japan’s prison population has not quite doubled to 71,000, while ours has quadrupled to 2.3 million.
The United States has by far the world’s highest incarceration rate. With 5% of the world’s population, our country now houses nearly 25% of the world’s reported prisoners. We currently incarcerate 756 inmates per 100,000 residents, a rate nearly five times the average worldwide of 158 for every 100,000. In addition, more than 5 million people who recently left jail remain under “correctional supervision,” which includes parole, probation, and other community sanctions. All told, about one in every 31 adults in the United States is in prison, in jail, or on supervised release. This all comes at a very high price to taxpayers: Local, state, and federal spending on corrections adds up to about $68 billion a year.
Our overcrowded, ill-managed prison systems are places of violence, physical abuse, and hate, making them breeding grounds that perpetuate and magnify the same types of behavior we purport to fear.
And Arlen Specter gets into details in an op-ed in the Philadelphia newspaper:
The U.S. criminalizes conduct that would be better left to treatment and penalties other than imprisonment. Take drugs. The number of jailed drug offenders has soared 1,200 percent since 1980 despite the fact that many of these offenders have no history of violence or high-level drug distribution. Many are behind bars under sentencing guidelines that leave judges no choice.In another example of dubious penology, too many mentally ill people are treated as miscreants or felons rather than as patients in need of treatment. There are four times as many mentally ill people in prison than in mental health hospitals. Many of these individuals end up back on the streets.
This is not about people convicted of violent crimes. We need to make sure that dangerous criminals and second-time offenders with a history of violence go to jail. As a former prosecutor who served two terms as D.A. in Philadelphia, I’m a strong proponent of incarcerating violent criminals for public safety and deterrence. And I support the death penalty in especially egregious cases.
But I also believe we need to restore judicial discretion in low-level drug cases and other nonviolent crimes. With our federal prisons at 140 percent capacity and with 7.3 million Americans incarcerated or on probation or parole – a number equivalent to 1 in every 31 adults – the issue cannot wait.
The question we started with, jail deaths in Lowndes County jail, is only a symptom. The problem is much larger. Fortunately, we can do something about it.
Georgia does not have a member on the Senate Judiciary Committee, but that means there’s no reason not to contact any or all of the members of that commmittee. Here they are.