Higher average temperatures
 mean much more frequent droughts and trees dying faster in droughts
because of the temperatures.
That plus pine beetles, according to research from 2009.
Forestry is Georgia’s second largest industry
in terms of
employment and wages and salaries,
more than $28 billion a year
according to the Georgia Forestry Commission,
plus an estimated
$36 billion a year in ecosystem services
such as water filtration, carbon storage, wildlife habitat, and aesthetics,
not to mention hunting and fishing.
Climate change matters to Georgia’s forests and to Georgia.
mean much more frequent droughts and trees dying faster in droughts
because of the temperatures.
That plus pine beetles, according to research from 2009.
Forestry is Georgia’s second largest industry
in terms of
employment and wages and salaries,
more than $28 billion a year
according to the Georgia Forestry Commission,
plus an estimated
$36 billion a year in ecosystem services
such as water filtration, carbon storage, wildlife habitat, and aesthetics,
not to mention hunting and fishing.
Climate change matters to Georgia’s forests and to Georgia.
The paper appeared 13 April 2009 in the Proceedings of the National Academy of the Sciences, Temperature sensitivity of drought-induced tree mortality portends increased regional die-off under global-change-type drought, by Henry D. Adams, Maite Guardiola-Claramonte, Greg A. Barron-Gafford, Juan Camilo Villegas, David D. Breshears, Chris B. Zou, Peter A. Troch, and Travis E. Huxman, 106(17) 7063-7066, doi: 10.1073/pnas.0901438106.
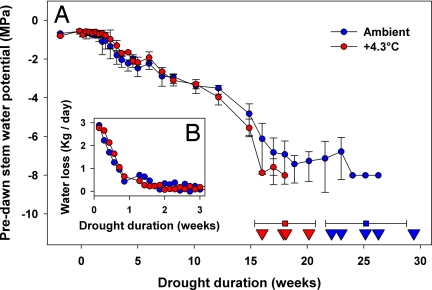
All drought trees in the warmer treatment died before any of the drought trees in the ambient treatment (on average 18.0 vs. 25.1 weeks, P <0.01; Fig. 1A).
They say warmer trees dying faster in drought wasn’t due to a difference in amount of water. Instead, they infer the warmer trees couldn’t breathe.
Combined, our results provide experimental evidence that piñon pines attempted to avoid drought-induced mortality by regulating stomata and foregoing further photosynthesis but subsequently succumbed to drought due to carbon starvation, not sudden hydraulic failure. Importantly, we isolate the effect of temperature from other climate variables and biotic agents
and show that the effect of warmer temperature in conjunction with drought can be substantial.
Our results imply that future warmer temperatures will not only increase background rates of tree mortality (13, 16), but also result in more frequent widespread vegetation die-off events (3, 35) through an exacerbation of metabolic stress associated with drought. With warmer temperatures, droughts of shorter duration—which occur more frequently—would be sufficient to cause widespread die-off.
How much more frequently?
They calculated an estimate for that, too: five times more frequently.
Of course, that’s for the specific kinds of forests they were studying,
and the exact number may vary, but the general trend is clear:
higher temperatures mean more frequent droughts,
like
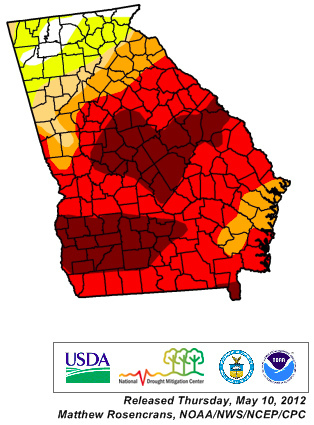 the year-long drought we just experienced in south Georgia.
the year-long drought we just experienced in south Georgia.
This projection is conservative because it is based on the historical drought record and therefore does not include changes in drought frequency, which is predicted to increase concurrently with warming (2, 37—39). In addition, populations of tree pests, such as bark beetles, which are often the proximal cause of mortality in this species and others, are also expected to increase with future warming (7, 9, 38).
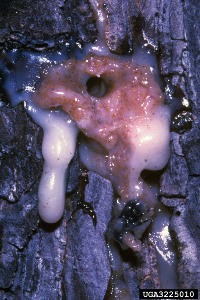
Bark beetles, such as the ones that bored into this 19 inch slash pine
and spread from there to twenty others I had to cut down to prevent further spread
of the pine beetles.
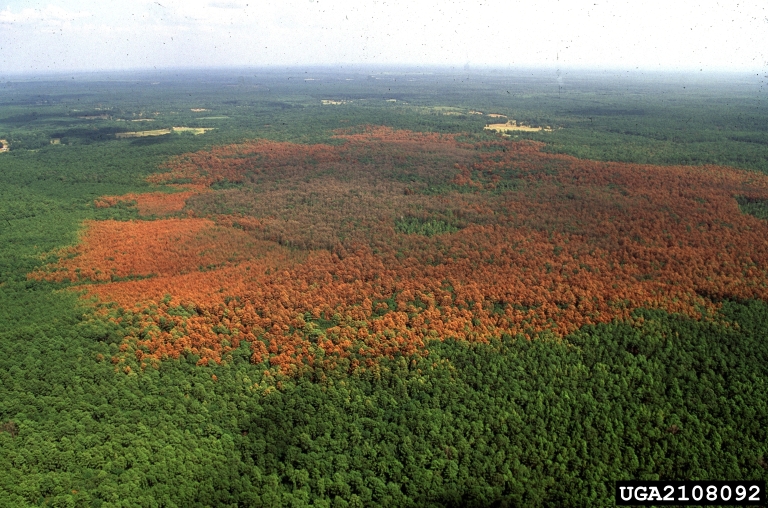
What happens when pine beetles spread
is what you see in the
first picture in this post:
acres and acres of dead red pine trees.
 Monoculture slash pine plantations may show this effect most clearly,
but look around here, and you’ll see red dead loblolly and longleaf pines,
too.
Monoculture slash pine plantations may show this effect most clearly,
but look around here, and you’ll see red dead loblolly and longleaf pines,
too.
The article is saying that if the beetles don’t get the trees weakened by droughts that will be much more frequent, the trees will die more quickly of suffocation, because the temperature is higher. Higher temperatures is something that should concern every Georgian in our state where forestry is the second largest industry and our forests protect our wildlife and the air that we breathe and the water that we drink.
-jsq





 Some people didn’t like the source of a recent post about
the toxic effects of agrochemicals and GM plants on the environment,
plants, animals, and people.
There are plenty of other sources, including:
Some people didn’t like the source of a recent post about
the toxic effects of agrochemicals and GM plants on the environment,
plants, animals, and people.
There are plenty of other sources, including:
