We’ve added 60 new solar PV panels to our old 20 panels at Okra Paradise Farms,
bringing our production up to about 15KW DC:
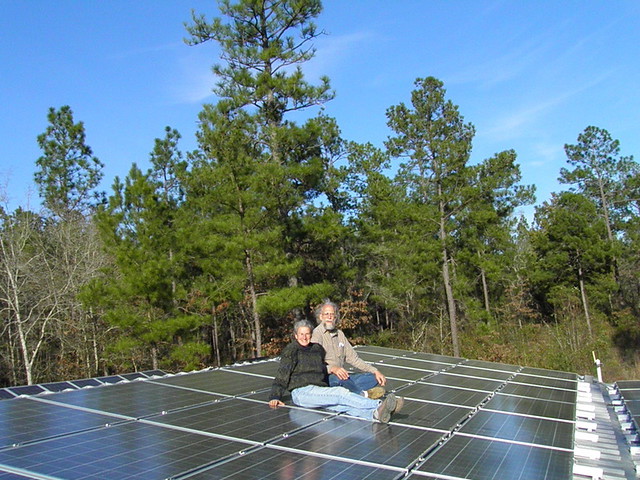

Gretchen Quarterman and John S. Quarterman on the new panels on the roof of the farm workshop at Okra Paradise Farms, Lowndes County, Georgia, 29 January 2012.
Photo CC BY-ND Okra Paradise Farms
You can see
the old panels sticking up on the left,
and we’re sitting on some of the new panels, which continue on the lower roof
on the right.
 These panels were purchased with the assistance of a
USDA Rural Energy for America Program (REAP) 25% grant:
These panels were purchased with the assistance of a
USDA Rural Energy for America Program (REAP) 25% grant:
Eligible projects include those that derive energy from a wind, solar,
biomass, or geothermal source, or hydrogen derived from biomass or water
using wind, solar, or geothermal energy sources.
The REAP program
will probably be renewed this year, so if you have a farm, you could apply.
 We also applied for and got a
We also applied for and got a
 U.S. Treasury 30% grant from the
1603 Program: Payments for Specified Energy Property in Lieu of Tax Credits.
That program was funded by the
The American Recovery and Reinvestment Act of 2009 (Recovery Act).
U.S. Treasury 30% grant from the
1603 Program: Payments for Specified Energy Property in Lieu of Tax Credits.
That program was funded by the
The American Recovery and Reinvestment Act of 2009 (Recovery Act).
Finally, there is the Georgia Environmental Finance Authority (GEFA) 35%
Clean Energy Property Tax Credit,
which will apply in parts over four years.
That all adds up to 90% covered by grants and tax credits,
which is a pretty good deal.
Now that remaining 10% is still a significant amount;
like the price of a small car.
But in 7-15 years (how long it will take to pay off this system,
depending on how you figure it),
what would
 the value of a car be?
Much less than when you bought it.
Meanwhile, these solar panels will be generating almost as much
power as they are now, and they will continue to generate for
at least a decade more, probably much more.
the value of a car be?
Much less than when you bought it.
Meanwhile, these solar panels will be generating almost as much
power as they are now, and they will continue to generate for
at least a decade more, probably much more.
The big missing piece is up-front financing.
For more on that, see other blog post.
Meanwhile, we have here on our workshop roof a proof of concept,
operational right now.
The little dogs wanted to know what we were doing on the roof:
Continue reading →
I will go over a few initiatives I am currently working on, specifically the StrikeForce Initiative (persistent poverty 60 counties), SET (Stronger Economies Together), and the significance of RHIT (Rural Health Information Technology). In the 2nd part I will be discussing some of our funding programs, focusing on Rural infrastructure, local foods, downtown development, and essential community facilities.